Informacje
ZEBRA FINCHES Taeniopygia guttata castanotis

WILD TIMOR ZEBRA FINCH

WILD ZEBRA FINCH

ZEBRA FINCH DOMESTIC

ZEBRA FINCH EXHIBITION TYPE
Basic information
The zebra finches belong to the genus Poephila of the Astrid family, belonging to the order of passerines.
There are two subspecies of zebra finches, the common zebra finch Poephila guttata guttata from eastern Indonesia and the Australian zebra finch Poephila guttata castanotis inhabiting continental Australia.
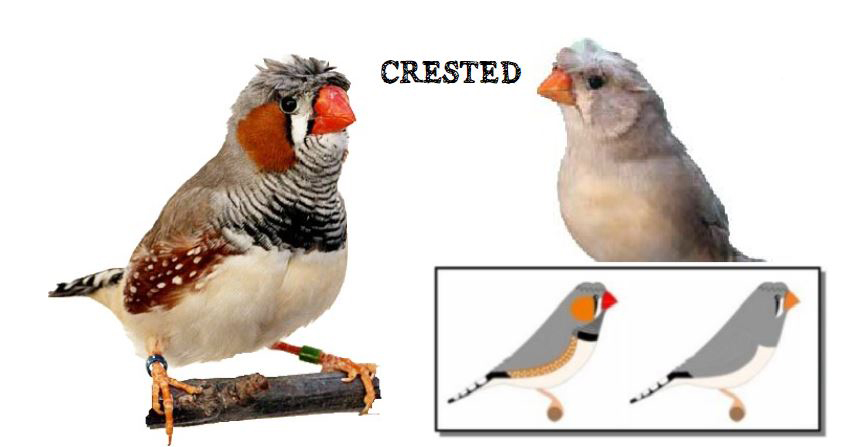
The Australian zebra finch is about 10cm in size and weighs 11g. Currently, there are 3 types of Australian zebra finches. The wild form, which occurs only in the natural environment, the breeding form does not differ in size from the wild zebra finch, but can occur in many color mutations.
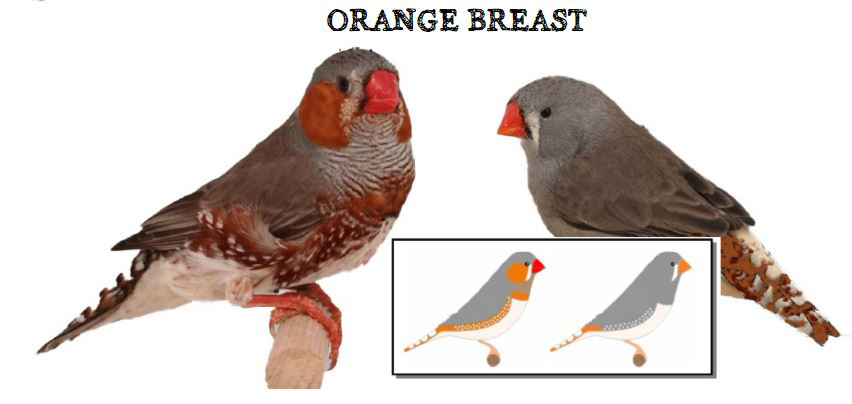
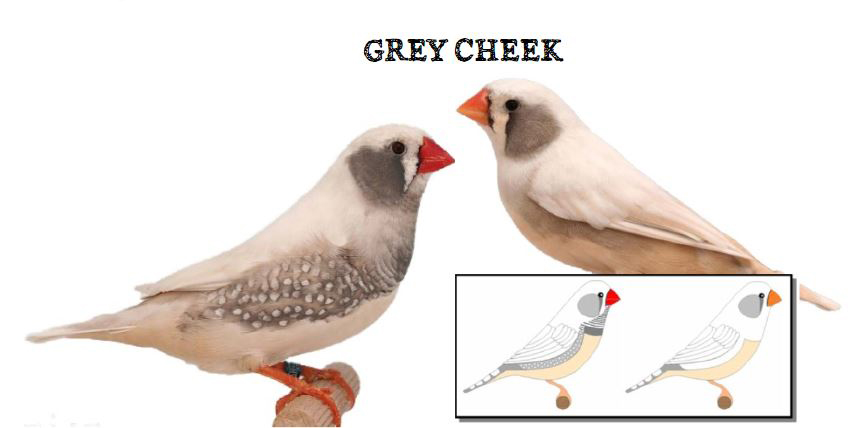
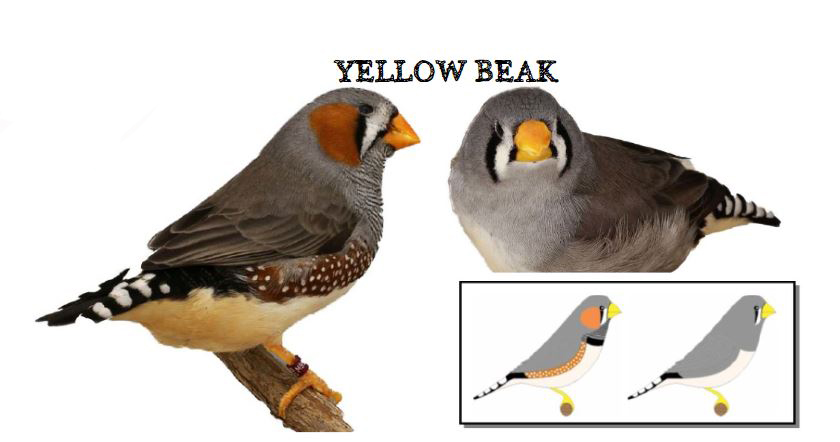
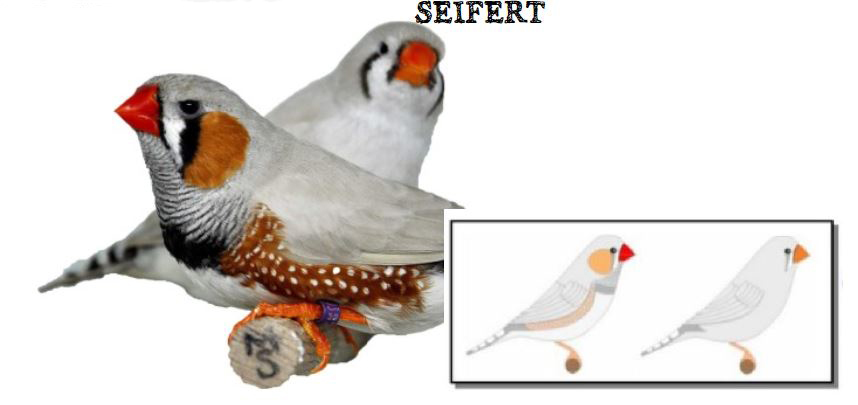
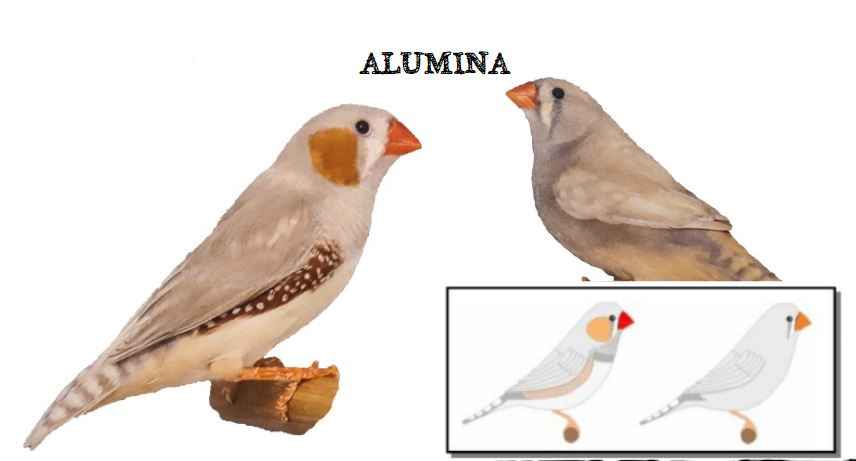
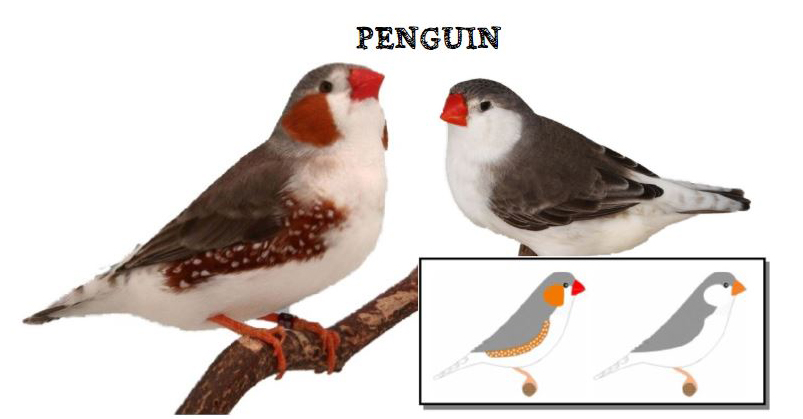
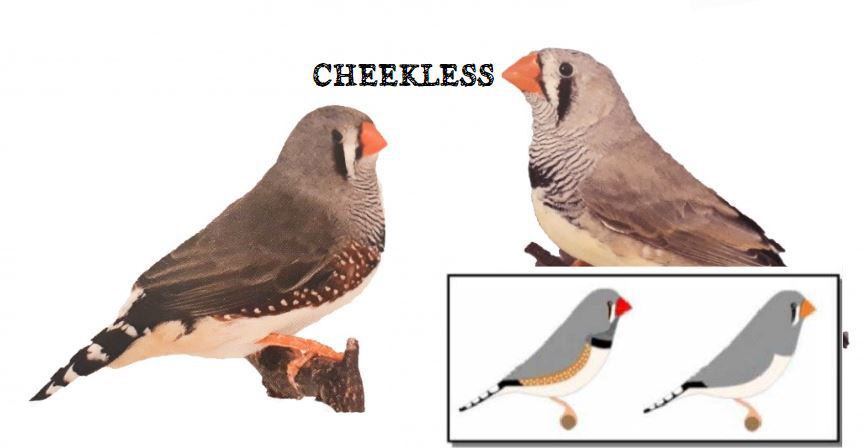
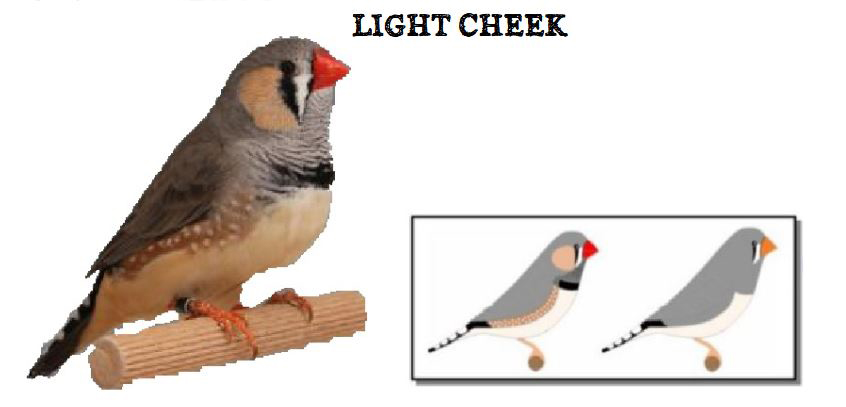
The last form is the show type, which differs significantly in size and build from the wild ancestor. Sexual dimorphism in the Australian zebra finch is very well marked. The standard male (wild feathered) is gray-brown in color with decorative rusty spots on both cheeks and black stripes on the subgradle and upper part of the breast, where there is a black spot (ruff).
On the sides of the body, under the wings, you can see brick-red feathers speckled with white dots. Another feature that distinguishes the male from the female is its intense ruby-red color of the beak. The female is much more modestly dressed, there are no colored spots on her cheeks in her plumage, and no ribbed dewlap with a ruff. The beak is usually pale red or orange in color. The female’s plumage is a mixture of gray and brown and is stripped of the typical male color ornaments. The nesting box for zebra finches should be 12x15x15 or 15x15x15cm. The nest material can be coconut fiber.
Australian zebra finches lay 4-6 white eggs on average. Both the male and the female brood their eggs. The incubation period is 12-13 days. The young leave the kennel after approximately 22 days and are further fed by their parents (approximately 14 days)
The food for the ribs is a mixture of grains consisting mainly of different varieties of millet, canary and grasses. During moulting, mating and breeding, it is worth supplementing the diet with animal food, e.g. egg mixture. Additionally, birds should have access to sepia as a source of calcium at all times.
An important addition to the diet of birds are green fodder in the form of, for example, starfish.
TYPES OF ZEBRA FINCHES FOR EXHIBITION
MALES

FEMALES

TYPES
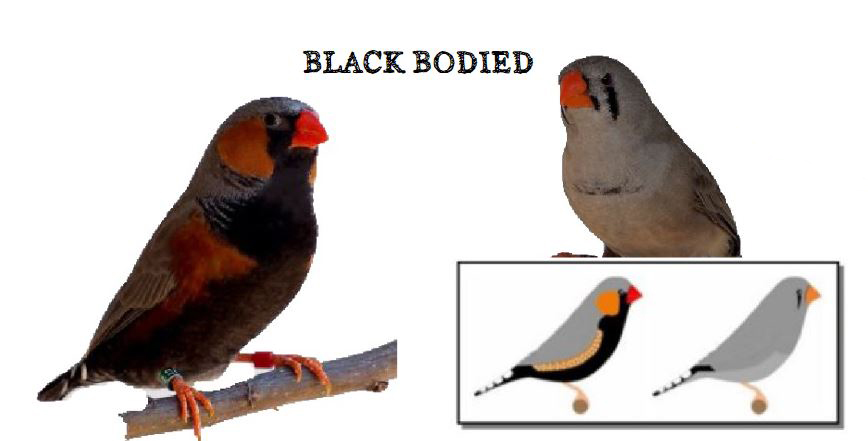
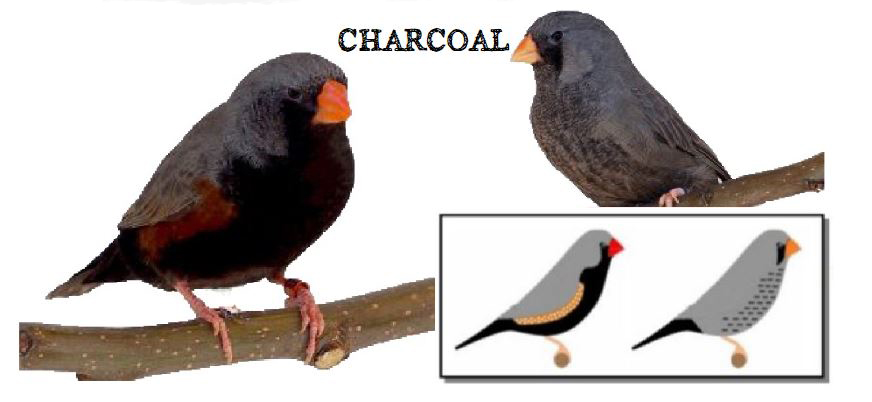
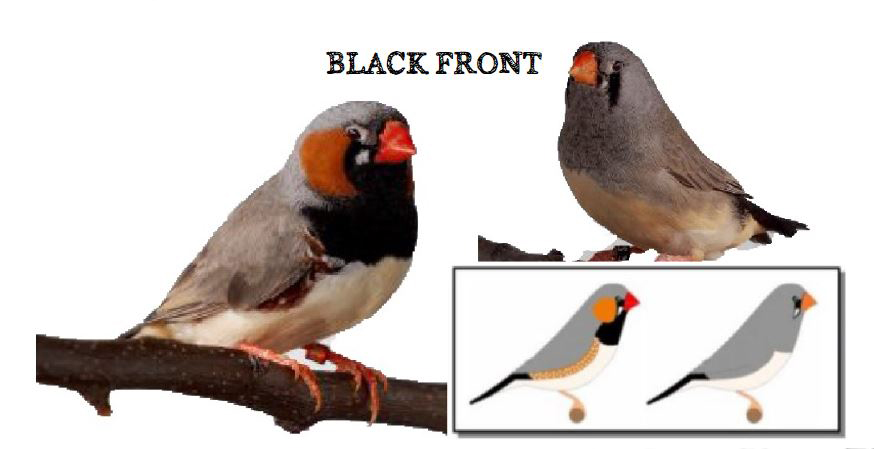
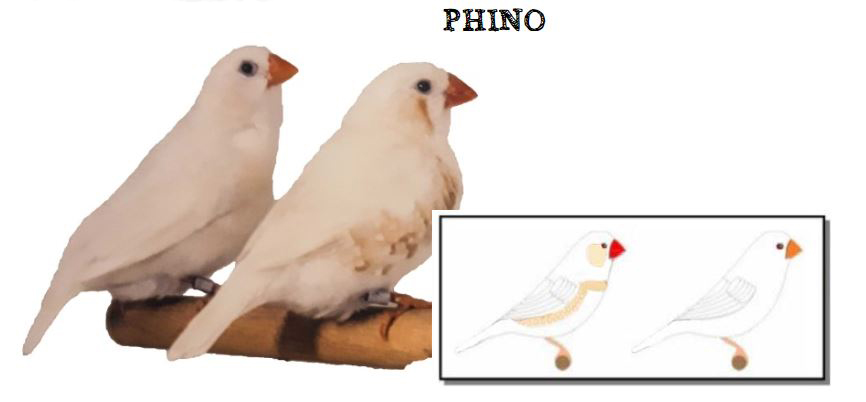
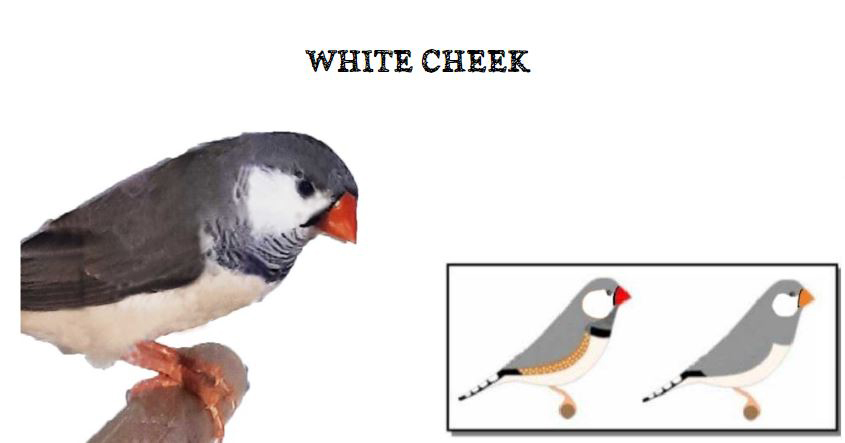
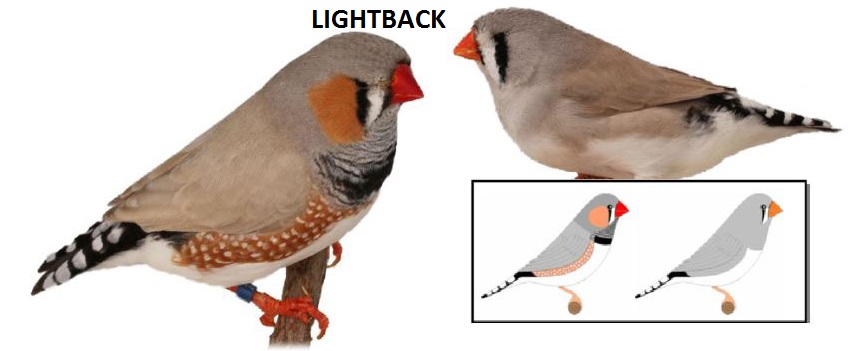
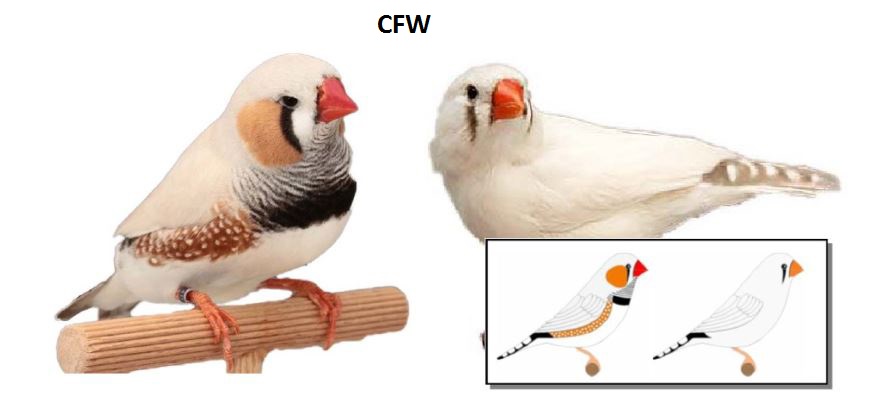
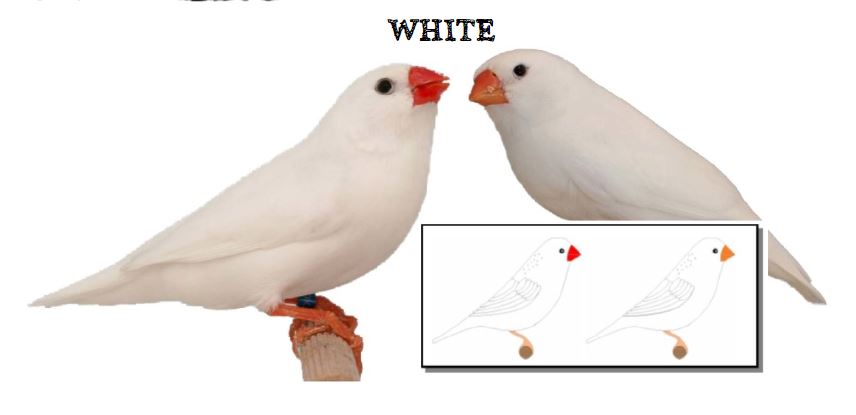
MUTATIONS
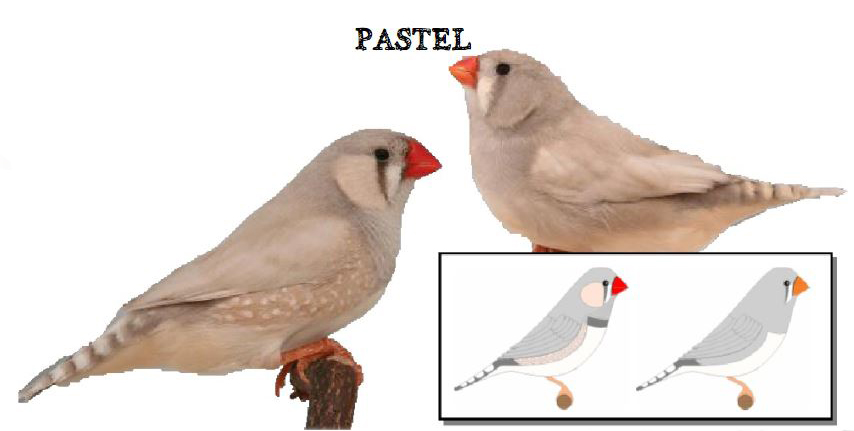
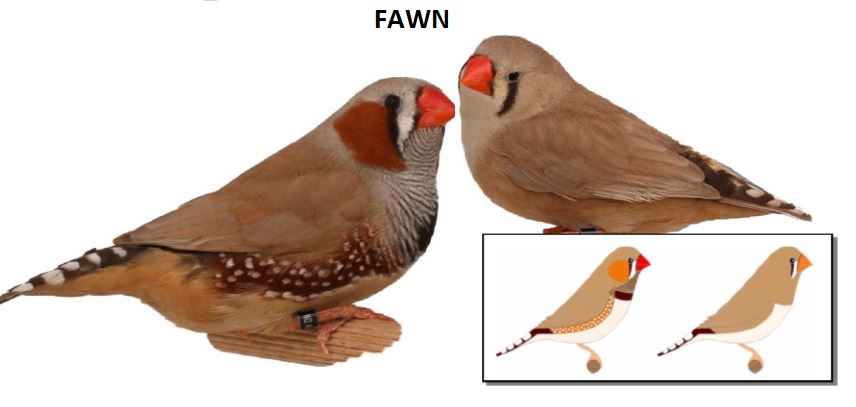
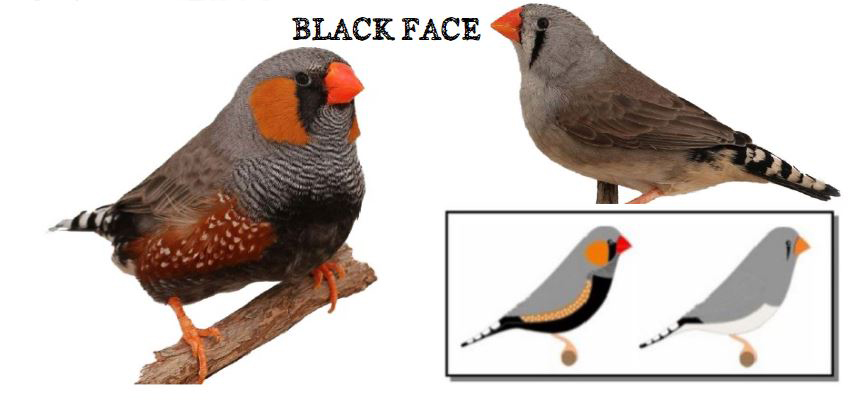










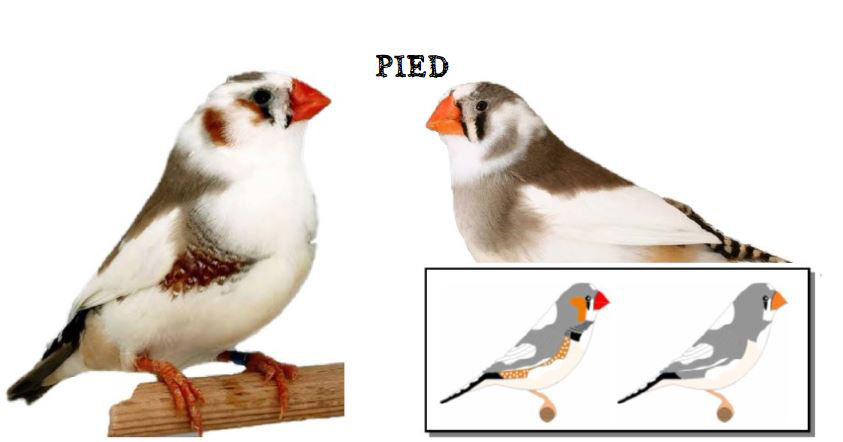
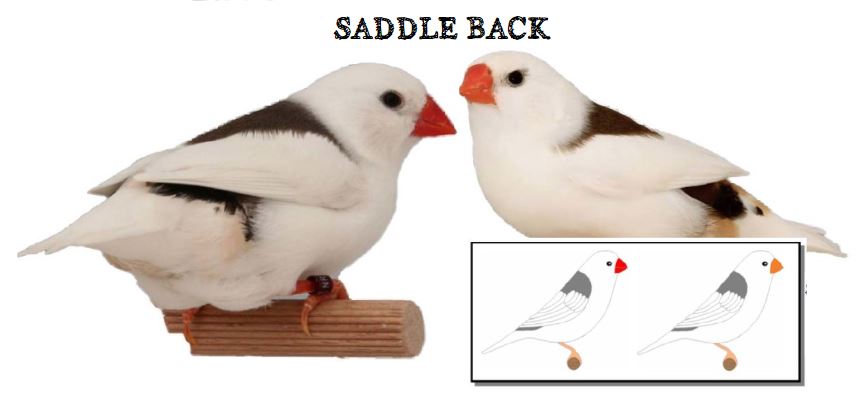



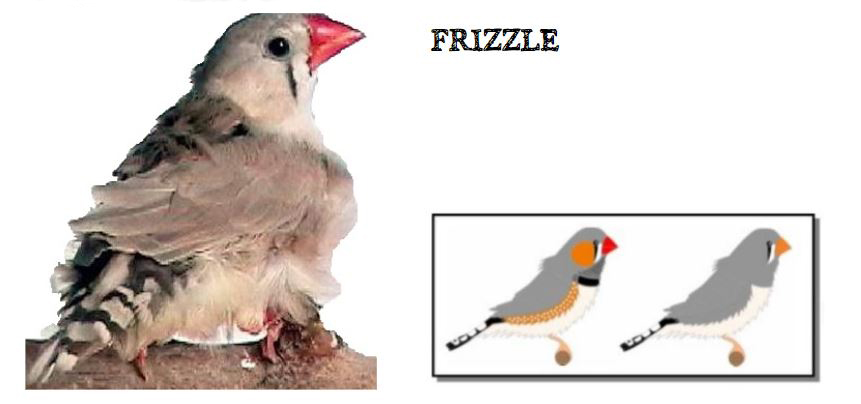
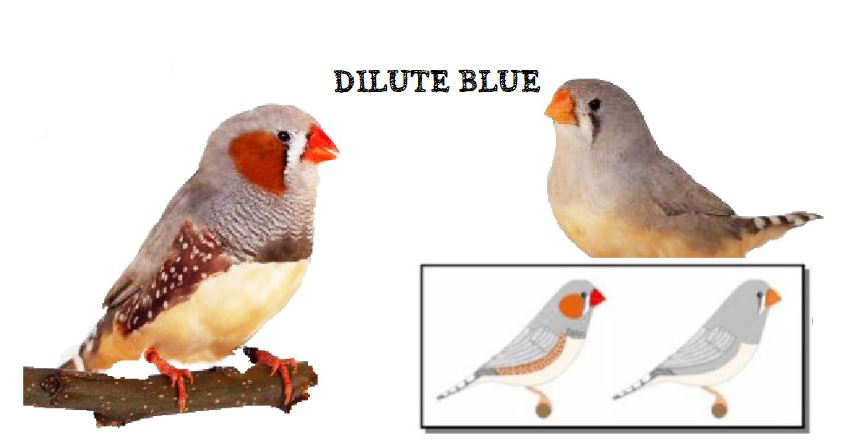

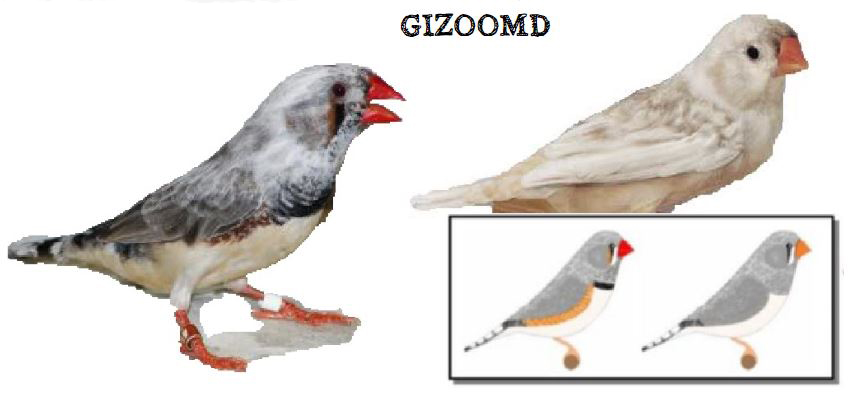












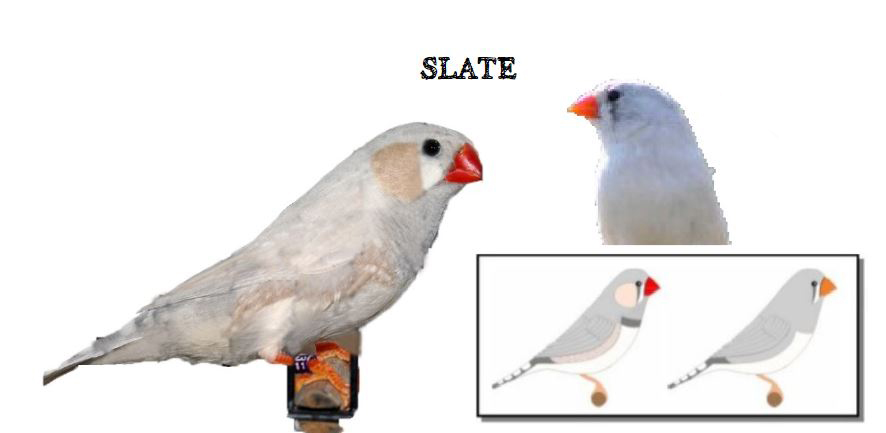
BREEDING PAIRS 2022










